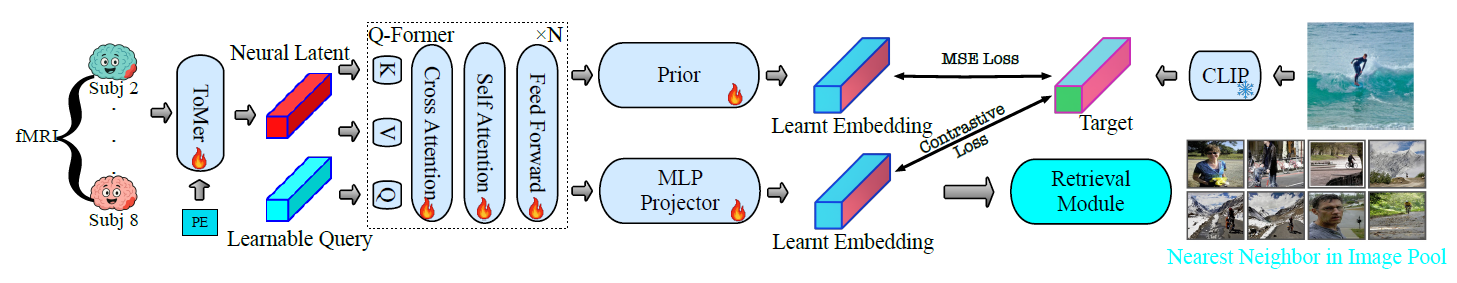
VoxelFormer: Parameter-Efficient Multi-Subject Visual Decoding from fMRI
VoxelFormer is a lightweight transformer architecture that enables multi-subject training for visual decoding from fMRI.

VoxelFormer is a lightweight transformer architecture that enables multi-subject training for visual decoding from fMRI.
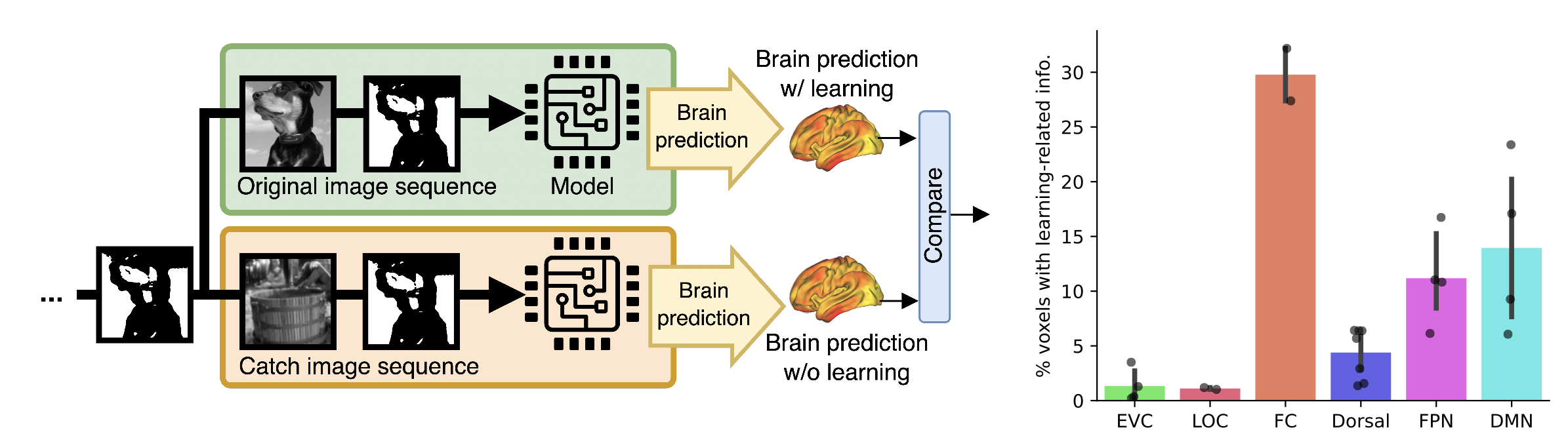
In this paper, we investigate the neural and computational mechanisms underlying one-shot perceptual learning in humans. By introducing a novel top-down feedback mechanism into a vision transformer and comparing its representations with fMRI data, we find high level visual cortex as the most likely neural substrate wherein neural plasticity supports one-shot perceptual learning.
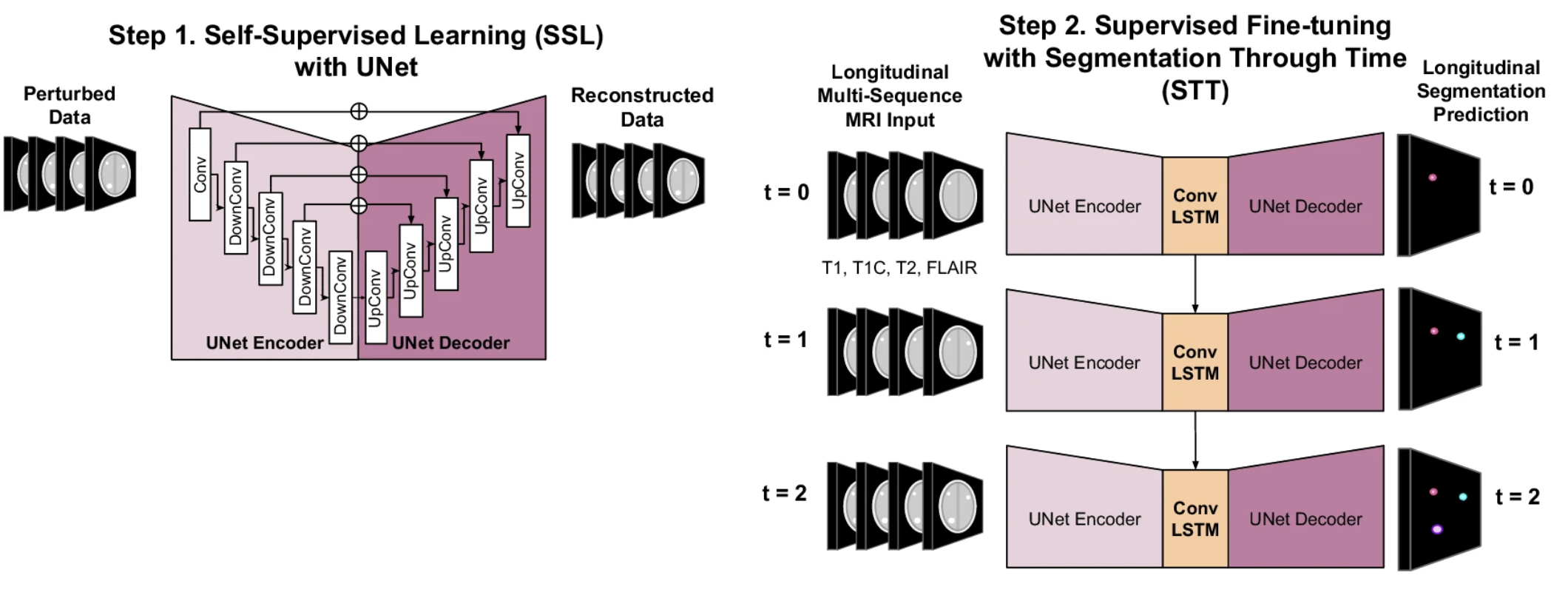
We present NYUMets-Brain, the world’s largest, longitudinal, real-world dataset of cancer consisting of the imaging, clinical follow-up, and medical management of 1,429 patients. Using this dataset we developed Segmentation-Through-Time, a deep neural network which explicitly utilizes the longitudinal structure of the data and obtained state-of-the-art results at small (<10 mm3) metastases detection and segmentation.
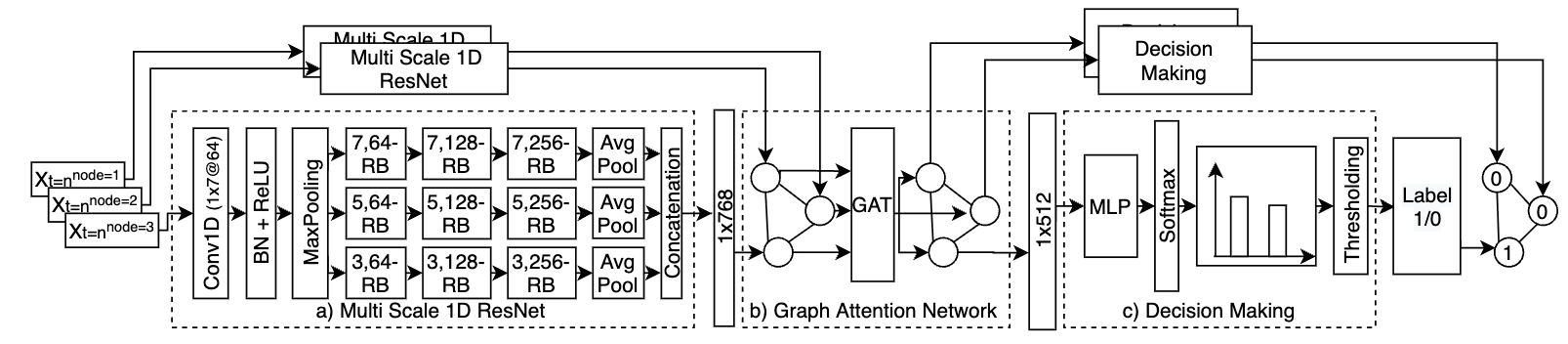
We present a graph neural network that is able to track cortical spreading depressions in scalp EEG signals. We show that our model is scalable to different densities of EEG and generalizable to different head models.